
The more complete and competent the diagnosis of prostatitis, the more effective the subsequent therapy. The approach of the official physician can result in long-term and ineffective treatment for the patient. Its job is to identify inflammation of the prostate and all the provoking factors.
How doctors diagnose prostatitis
Prostatitis is diagnosed by a urologist or andrologist. After talking to the patient, the doctor will prescribe the necessary tests: first a standard set (blood, urine, prostate secretions, rectal examination) and then, if necessary, more detailed and high-tech methods will be used: CT, MRI, ultrasound.
Record history
During the first consultation, the doctor will ask the following questions:
- Duration of intercourse (if shorter, under what circumstances);
- Discomfort in the groin after prolonged static strain and after alcohol or hypothermia
- Frequency and speed of urination (are there difficulties, intermittent jets, do you have to get up often to use the toilet at night);
- Orgasmic quality (still light or blurred, painful ejaculation).
The more details the patient remembers, the more complete the clinical picture taken by the physician will be.
Differential diagnostics
The symptoms of prostatitis are similar to those of many other diseases:
- Cystitis (cramps when urinating, pain in the lower abdomen).
- Adenoma (difficulty urinating, feeling of difficulty in the groin).
- Prostate cancer (blood in the urine, urinary problems).
- Rectal pathologies: hemorrhoids, paraproctitis (inflammation), anal fissures, creptitis (ulcerative colitis).
Table 1 shows additional diagnostic methods and their rationale.
Table 1: Differential diagnosis of prostatitis
| Disease | Risk Group | Analyze |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperplasia | Men over 45 years of age with no history of urethritis, catheterization, bladder and urethral trauma (conditions that may explain pain, blood in the urine) | Prostate ultrasound and digital examination |
| Prostatitis | Mostly young men who have recently had a fever, hypothermia with no provocative history (identical to hyperplasia) | Ultrasound, Whole Blood Count (CBC), Digital Prostate Examination |
| Prostate cancer | Men over 45 with no history of provocative factors | Prostate ultrasound, PSA analysis, digital examination |
If necessary, other specialists will be involved in the diagnosis: proctologist, neurologist, vertebrologist. The last two experts identify the causes of pain associated with violation of the structure of the spine, violation of nerve endings.
Rectal palpation
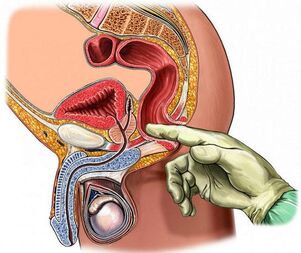
Digital rectal examination is the most accessible and informative method for checking the condition of the prostate. During the procedure, the doctor pays attention to the following parameters of its structure:
volume- ;
- Density;
- Surface roughness;
- Homogeneity (tissue homogeneity);
- Boundaries (clarity of outline);
- Preservation of the isthmus (longitudinal seam between the lobes).
In prostatitis, the gland enlarges due to edema (asymmetry is possible), its texture is flexible, the longitudinal groove (suture) is not palpable, and the patient may feel pain when touched.
A clear picture of this type of diagnosis requirespreparation:
- Do not ejaculate the day before, do not drink alcohol, avoid heavy physical exertion, hypothermia and overheating.
- Do not ride a bicycle for a day, do not use a rowing machine (do not injure or massage the prostate in this way).
- Before visiting a doctor, make an enema (micro enema can be used) to clean the rectal ampoule.
The prostate can be felt 3-5 cm deep from the anus. The doctor performs the procedure with sterile gloves, smearing the finger with gel. The patient is lying on his side with his knees down or in a knee-elbow position.
Laboratory Methods
Laboratory methods for diagnosing inflammation of the prostate include testing biological agents for the presence of pathogens.
Blood
Based on the results of general and biochemical blood tests (take a capillary from your finger), prostatitis is suspected at an early stage. The analysis is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. You should refrain from smoking an hour before the procedure.
Key Indicators:
- Leukocytes (blood cells that increase in number as immunity decreases in the background of inflammatory reactions). Normally 4-9 × 10 ^ 9 units;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). The norm is around 5 units, the increase indicates inflammation or an oncological process;
- Lymphocytes. Normally, their percentage in the total volume of blood cells ranges from 18 to 40 units. Exceeding means infection.
Men over the age of 40 are prescribed a PSA test- a tumor marker with a value greater than chronic prostatitis or prostate cancer.Norm- less than 4 ng / ml, after 50 years - 5. 53 ng / ml.
Urine
The urethra passes through the prostate (part of the prostate of the urethra) so that when the gland becomes inflamed, the urine changes color and texture. Three types of analysis are performed to diagnose prostatitis:
- General - determination of physical and chemical parameters. Signs of inflammation of the prostate: urine is cloudy, whitish, alkaline, there is protein, leukocytes, purulent fibers, sometimes foam or blood. Phosphates are present in calcite prostatitis.
- Investigation of the presence of cytologically - abnormally altered cells. The presence of erythrocytes and epithelium may indicate a tumor process.
- Bacteriological - identification of traces of activity of pathogenic microorganisms. To do this, make a container that sows sediment on the medium. If there are bacteria and fungi, they will start to multiply actively after a while. Escherichia coli often provokes inflammation of the prostate.
Before urinating, refrain from consuming salty and spicy foods, do not consume alcohol and coloring products (beets, coffee). The analysis is taken on an empty stomach in the morning.For inflammation of the prostate, the three-glass test method is used:the patient takes turns urinating in each glass; the result is the first, middle and last part. This method makes it possible to identify the location of inflammation: urethra, prostate, bladder. The four glass methods are more informative. The last part of the urine is collected after the prostate massage to obtain its secretion.
Prostate secretion and sperm
Prostate juice is a valuable diagnostic substance. Prepare for your fence just as you would for a rectal digital examination. In order for the amount of secrecy to be sufficient, you must refrain from sexual intercourse for three to five days.
Methods for examining prostate secretion:
- Microscopy;
- Rewind;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
PCR is the most accurate method. Special enzymes are used to process biological materials, which multiply the number of DNA and RNA fragments of pathogens. Research requires a special tool - an amphipath. The most accurate real-time PCR. The result is ready in an hour.
Inflammation of the prostate in the juice is indicated by amyloid bodies, staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, epithelial cells (more than three units in the field of view). The number of lipoid particles decreases and the number of leukocytes increases.
Thespermogram of prostatitisis an additional analysis. Against the background of inflammation of the prostate, the sperm is yellowish or brownish in color, its viscosity increases (liquefies for a long time), and a pathogenic microflora is present. In chronic prostatitis, epithelial cells of the gland, amyloid bodies, and mucus are found.
Urethral swab
The urethral swab (scraping) is a less informative method of diagnosing prostatitis than secretion analysis.It is used in cases where the latter is impossible to obtain due to hemorrhoids, worsening of inflammation, the presence of calcifications in the prostate body.
The metabolic process is quick but inconvenient: the doctor immerses a brush in the urethra, which, along with microorganisms, traps some of the cells that cover it. The biological material is then examined by PCR, which allows the presence of pathogens in any amount to be determined. The cause of prostatitis can be genital infections: chlamydia, Trichomonas, mycoplasma.
Before performing the analysis for a day, you should reject sexual intercourse, perform only external hygiene procedures for the penis in the morning (do not pour anything into the urethra), and do not urinate for two hours.
Instrumental methods
Instrumental diagnostic methods make it possible to confirm and supplement the results of laboratory tests.
Ultrasound and TRUS
Ultrasound of the prostate allows the visualization of its structure, contours, and the nature of tissue changes. In the case of prostatitis, transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is considered the most informative: the doctor inserts a transducer into the rectum. Prepare for the procedure in the same way as you feel the gland. Abdominal ultrasound (through the abdomen) is more comfortable for a man, but the prostate is not fully visible due to the bladder.
With inflammation of the prostate gland, its structure is heterogeneous, the contours are blurred, there may be foci of fibrosis (overgrown connective tissue), scars. The prostate is enlarged, the groove between its lobes is balanced.
MRI, PET, and CT
If ultrasound gives rise to suspicion in the presence of a tumor process, your doctor will prescribe CT (computed tomography) or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) prescriptions. . This latter type of research is more accurate but also more expensive. The procedures are painless and can replace biopsy (squeezing a piece of tissue) in terms of the content of the information.
CT and MRI show in detail the structure of the prostate: stones, cysts, tumors, inflammatory foci, structural disorders. For a clearer picture, the contrast agent is pre-injected into a vein (not used in men with kidney failure). The appropriate type of tomograph and rectal probe are used for the procedure.
PET - positron emission CT. It allows the analysis of the state of the prostate at the cellular and molecular levels. This determines not only the presence and size of the tumor, but also the speed and quality of the metabolic processes that take place in it.
On preparation:rectal should be emptied. Do not eat for five hours before the procedure.
Characteristics of the diagnosis of certain types of prostatitis
Acute bacterial (infectious) prostatitis is diagnosed on the basis of patient complaints, urinalysis, ultrasound, urethral smear. In case of active inflammation, painful, transrectal interventions of the gland are not allowed, in extreme cases careful finger examination.
Laboratory data for the diagnosis of acute prostatitis are not very informative. Urine culture may be advisable but not necessary. In the case of active inflammation, there is no time to wait for results. Antibacterial therapy with broad-spectrum drugs is performed to relieve symptoms.
Chronic prostatitis is practically non-existent, so its detection requires a whole range of laboratory, physical, instrumental methods. It may be necessary to determine the immune and neurological status of the patient.
Tactile secretion of the gland, urine, and prostate is of primary importance. The presence of more than 10 leukocytes in the field of vision indicates inflammation. If the bacterial culture does not show an increase in the infectious microflora in the background of increased leukocytes, then analysis for genital infections is required.
Due to the bacterial nature of inflammation, a large number of pathogens are found in urine and prostate juice. An undeniable microbiological sign of chronic inflammation: the number of microbes (CFU) is more than 104 / ml. Some of them are listed in dozens, so their presence in the amount of 10-102 / ml may indicate prostatitis.
Absent in the case of bacterial (non-infectious) inflammation, but experts recommend a deeper analysis in such cases: a prostate defect through which pathogens living in closed prostate passages are extracted. However, the bacterial culture is sterile, but the pathogen is eventually found. It is most often a type of E. coli.
Ultrasound does not always show chronic inflammation. In addition to the methods mentioned above, your doctor may prescribe uroflowmetry - a measurement of urine flow rate using special sensors.
Typical comorbidities
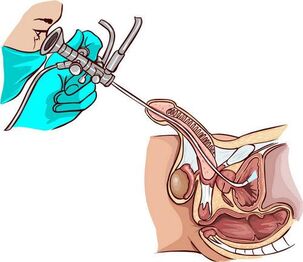
In case of chronic chronic prostatitis with signs of colliculitis (inflammation of the tuberculosis of the eye next to the prostate),urethroscopy is used - a visual examination of the canal with an endoscopic device. It helps to identify urethral stenosis, violation of its structure, the condition of the prostatic drainage channels (mucus, pus, thickening) and openings in the tuberculosis of the eye cavity.
Interpretation of results (determination of stages of prostatitis based on the state of the sex tuberculosis:
- First: the tuber is red, edematous, bleeding. The same pattern is observed in the back of the urethra;
- Second, there is a periodic increase and decrease in erythema and swelling;
- Third, there are cicatricial changes in the tissues of tuberculosis and urethra, which can cause the lumen of the ureter to narrow (narrowing).
Ureteroscopy irritates the tubercle receptors in the eyelid, leading to impaired microcirculation and prostate motility, so the procedure is not performed unnecessarily.
Cystitis is also a concomitant of chronic prostatitis. Inflammation of the bladder wall is detected by ultrasound andcystoscopy. The research identifies abnormalities of the mucous membranes, especially in the neck area. Bladder status in the background of chronic prostatitis (prostate sclerosis):- Cicatricial deformity of the bladder triangle.
- Dilated ureteral openings.
- Neck narrowing.
Cystoscopy is prescribed as early as the last stage of the study in the presence of lower abdominal pain and frequent urination.
Chronic, bacterial prostatitis with pelvic pain of unspecified origin is the most difficult to diagnose. In such patients, physicians first conduct research to rule out cystitis and neuropsychiatric pathologies.
How to diagnose prostatitis at home
A person may suspect acute prostatitis with the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen and groin (between the testicles and the anus);
- Increased body temperature;
- Pain when urinating (like cystitis);
- Premature and painful ejaculation.
The same symptoms occur during exacerbation of chronic prostatitis caused by hypothermia or alcohol consumption. The development of this pathology may be evidenced by the periodic appearance of blood in the urine, dull pain in the perineum (especially in a static position), difficulty urinating, deterioration of erection. Such signs cause contact with the urologist.
Conclusion
The longer the inflammatory process in the prostate lasts, the more difficult the treatment will be, so you should not delay the diagnosis. In government institutions, most procedures and aftercare are free.
























